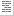|
Servlets
Java Servlets is a new form of scripting that is gaining popularity
because it allows portable server extensions that do not rely on
starting external binaries. Servlets are written in Java and compiled
to Java byte code before they can be used in a web server.
In Challenger, Servlets are supported through the Java
servlet bridge module, which transforms a Servlet into a
Location Module. The Java servlet bridge module can
have any number of copies, so any number of Servlets can be installed
on a single virtual server.
To run the Servlet support you need a Pike that has been compiled
with Java support. The binary versions of Challenger are not compiled
for Java support. To compile a Pike with Java support you have to
install JDK 1.2 and then compile Pike. Pike's Java module should
detect the Java environment automatically.
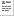
Java servlet bridge
- Class name
-
The name of the Java class implementing the
Servlet. The module will look for the corresponding .class
file in the Code directory (see below).
- Code directory
-
The location of the .class
files for this Servlet in the real file system. The path is relative
to the server directory. Multiple Servlets can reside in the same code
directory, as long as they have unique class names.
- Parameters
-
Servlet-specific parameters can be set
here, see the documentation of the Servlet in question to find out
what parameters it supports. Each parameter must be placed on a
separate line, with the name and the value separated with an equal (=)
sign.
- Servlet location
-
This Servlet's location in the
virtual file system. Any URL starting with this prefix will be handled
by this Servlet. The rest of the URL will be provided to the Servlet
as "Path Info".
Note that reloading the bridge module will reload the Servlet itself
from its .class files as well, which can be useful when
developing new Servlets.
|